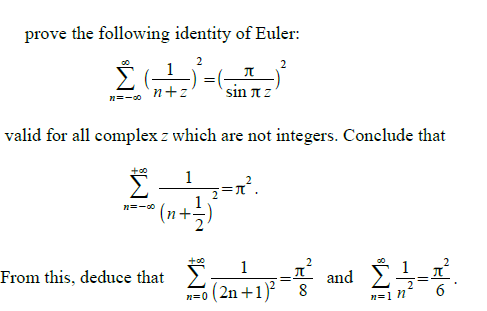
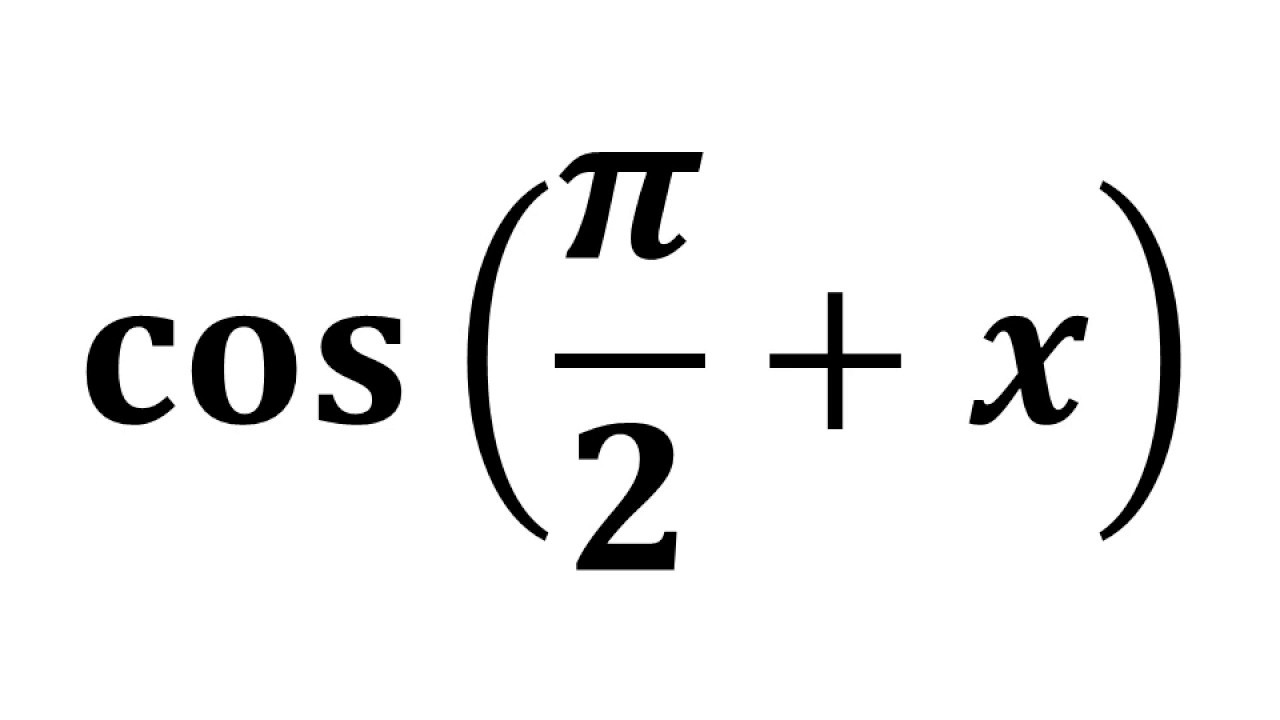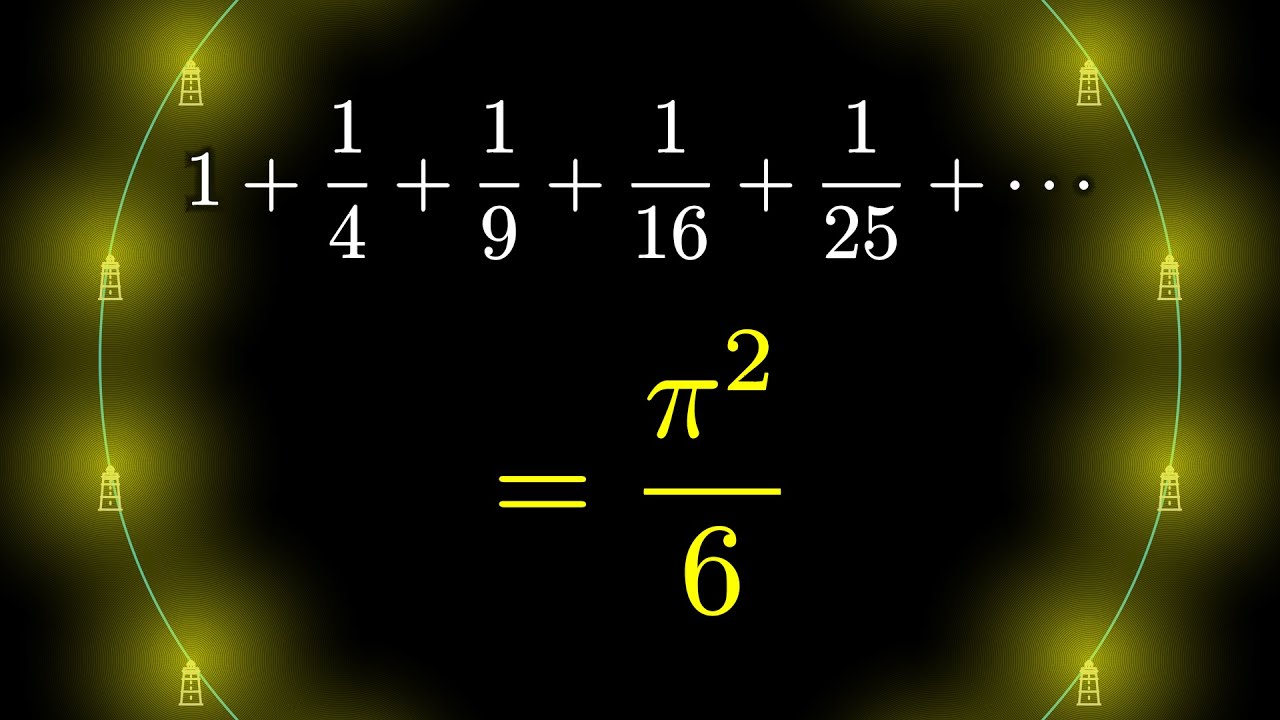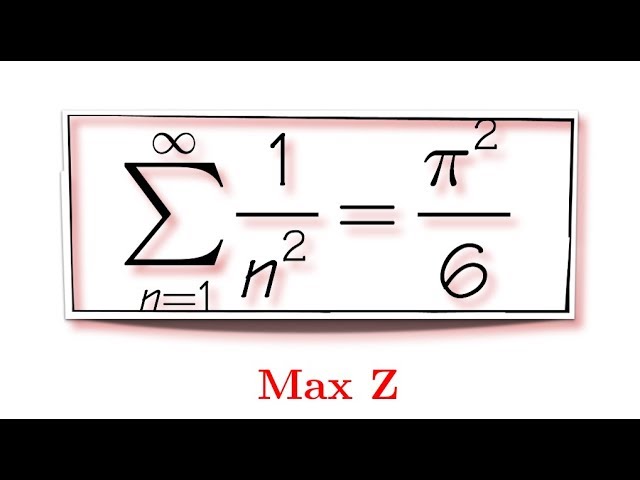sequences and series - Why does the sum of inverse squares equal $\pi^2/6$? - Mathematics Stack Exchange

sequences and series - Proof of $\frac{1}{N}\sum_{j=1}^{N}{\sin(jx)}<\frac{2}{Nx}, \forall x \in (-2\pi,2\pi)$? - Mathematics Stack Exchange
What's an intuitive explanation of the following mathematical fact: [math]\displaystyle \sum_{n=1}^{\infty}{\frac{1}{n^2}} = \frac{\pi^2}{6}[/math]? - Quora