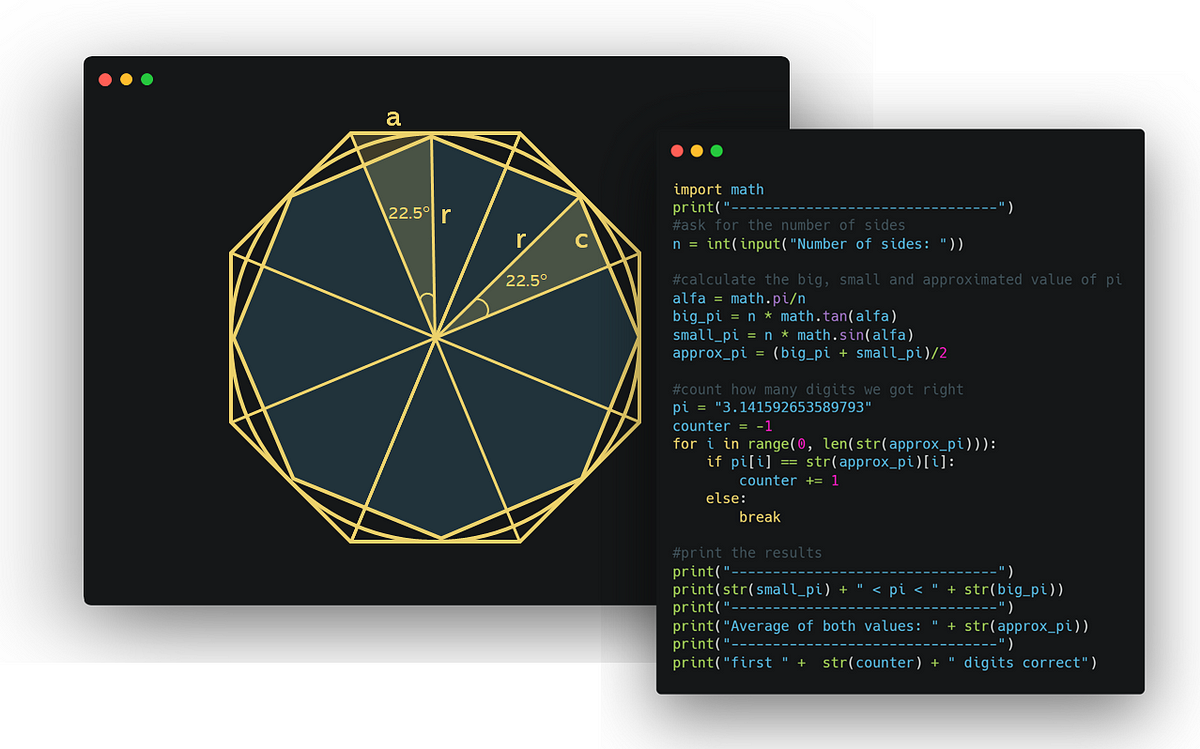
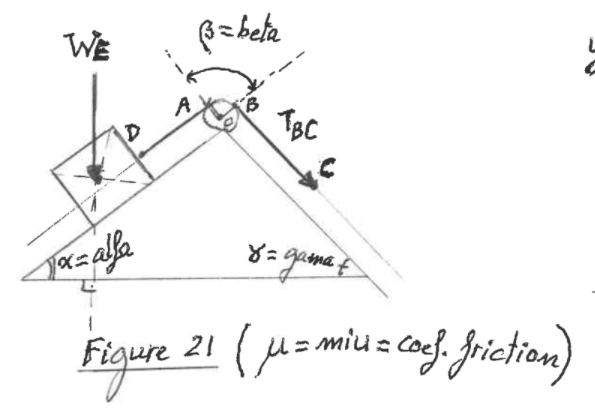
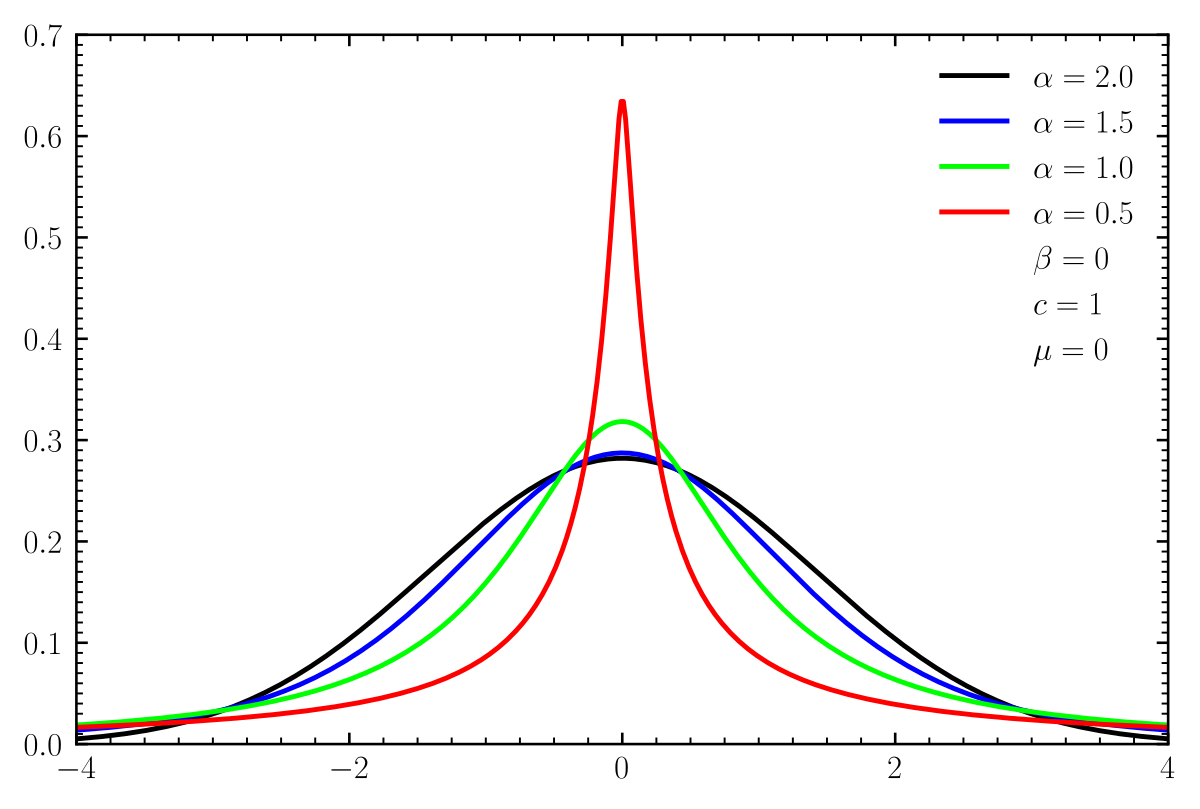
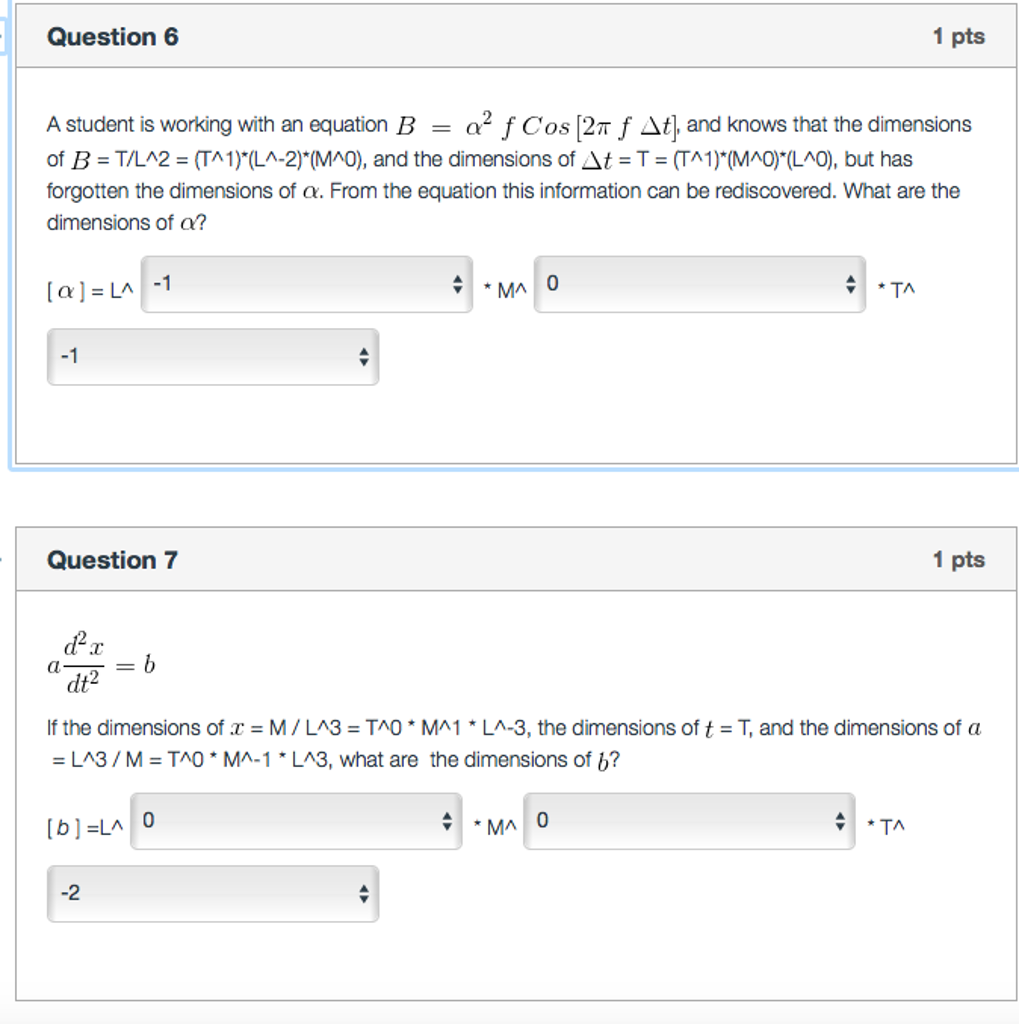
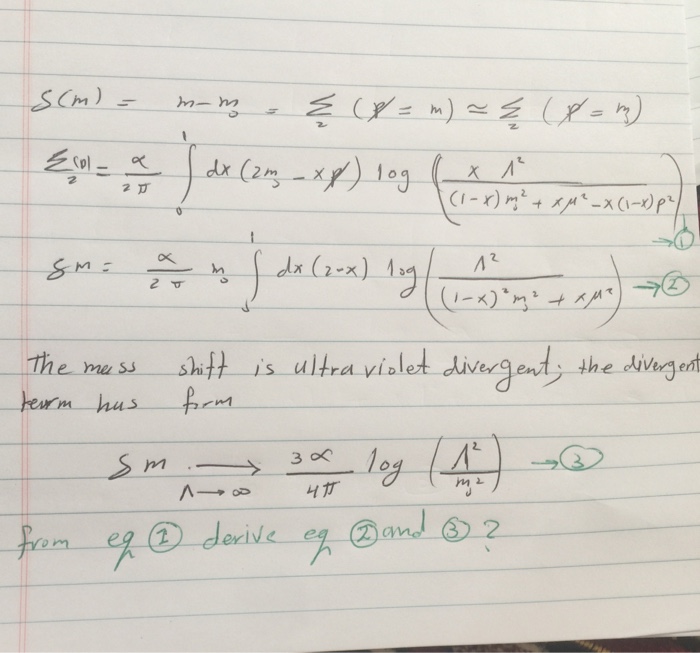Let f : (0, pi)→ R be a twice differentiable function such that limit t→x f(x)sint - f(t)sinxt - x = sin^2x for all xepsilon (0, pi) .If f (pi6) = -
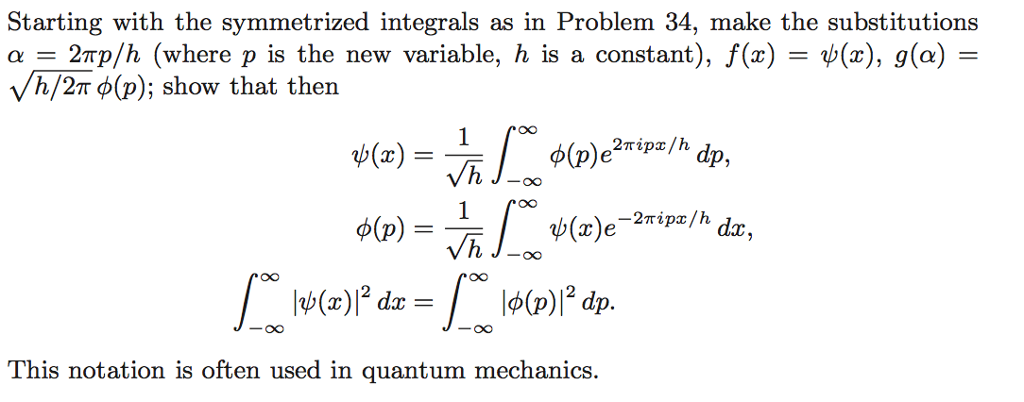
![Match the function with its graph. State the period of the function. [The graphs are labeled (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f).] \qquad y = -2\sec(\pi x/2) \, (a) src='6682280-556417884486163178157.png' alt='' Match the function with its graph. State the period of the function. [The graphs are labeled (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f).] \qquad y = -2\sec(\pi x/2) \, (a) src='6682280-556417884486163178157.png' alt=''](https://homework.study.com/cimages/multimages/16/6682280-556417884486163178157.png)
Match the function with its graph. State the period of the function. [The graphs are labeled (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f).] \qquad y = -2\sec(\pi x/2) \, (a) src='6682280-556417884486163178157.png' alt=''
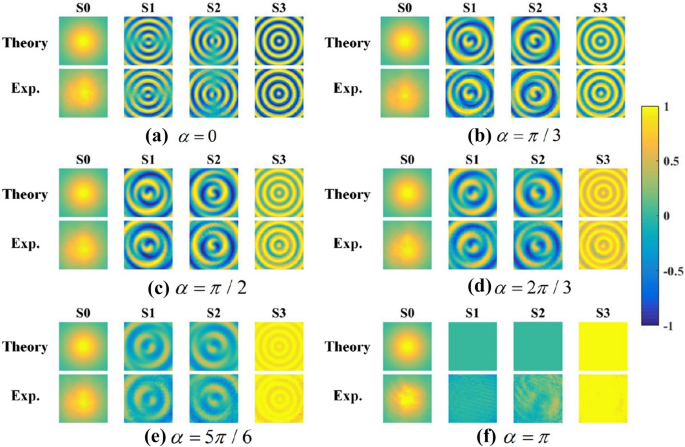
Unitary transformation for Poincaré beams on different parts of Poincaré sphere | Scientific Reports

If sin A = 4/5,pi/2<A<pi and cos B = 5/13,3pi/2<B<2pi , find (i) sin (A + B) , (ii) cos (A - B) , (iii) tan (A - B)

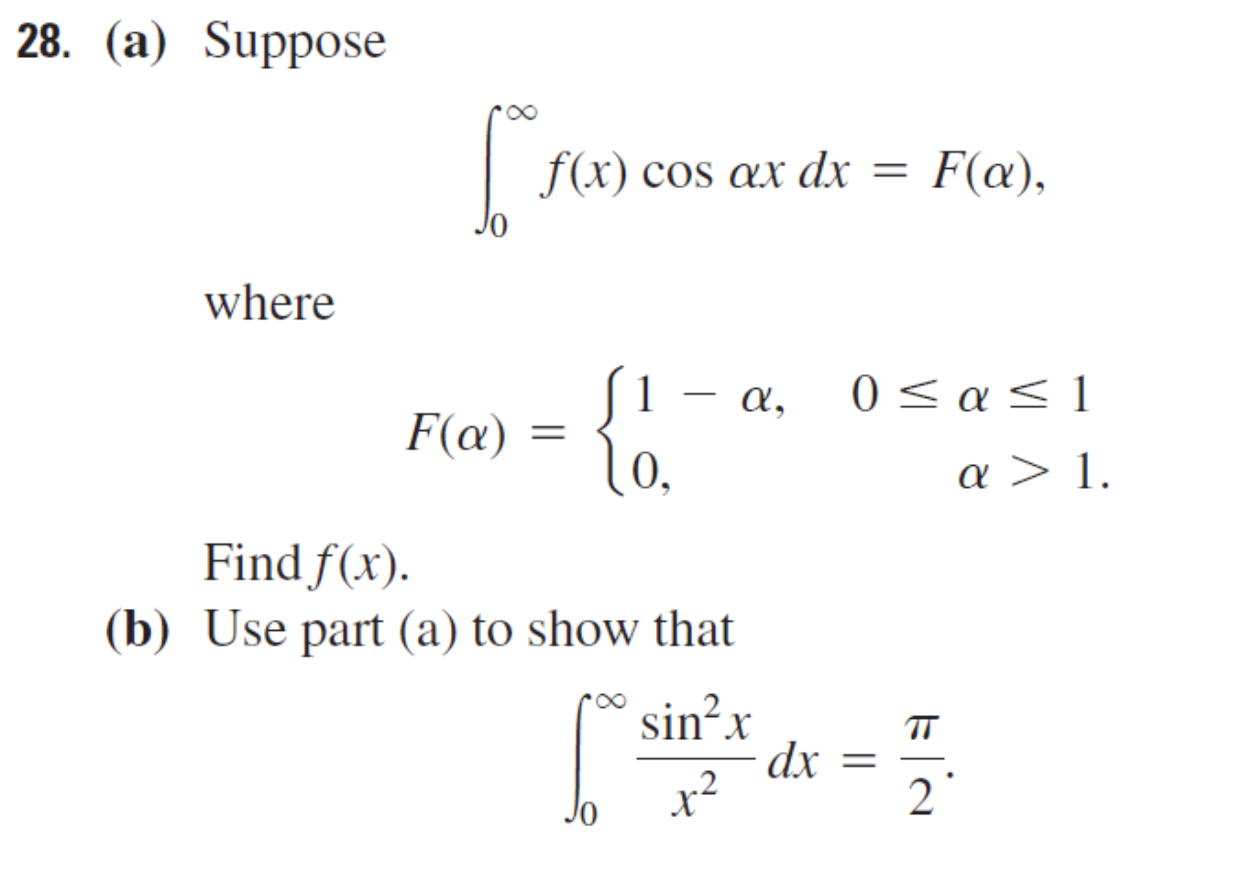

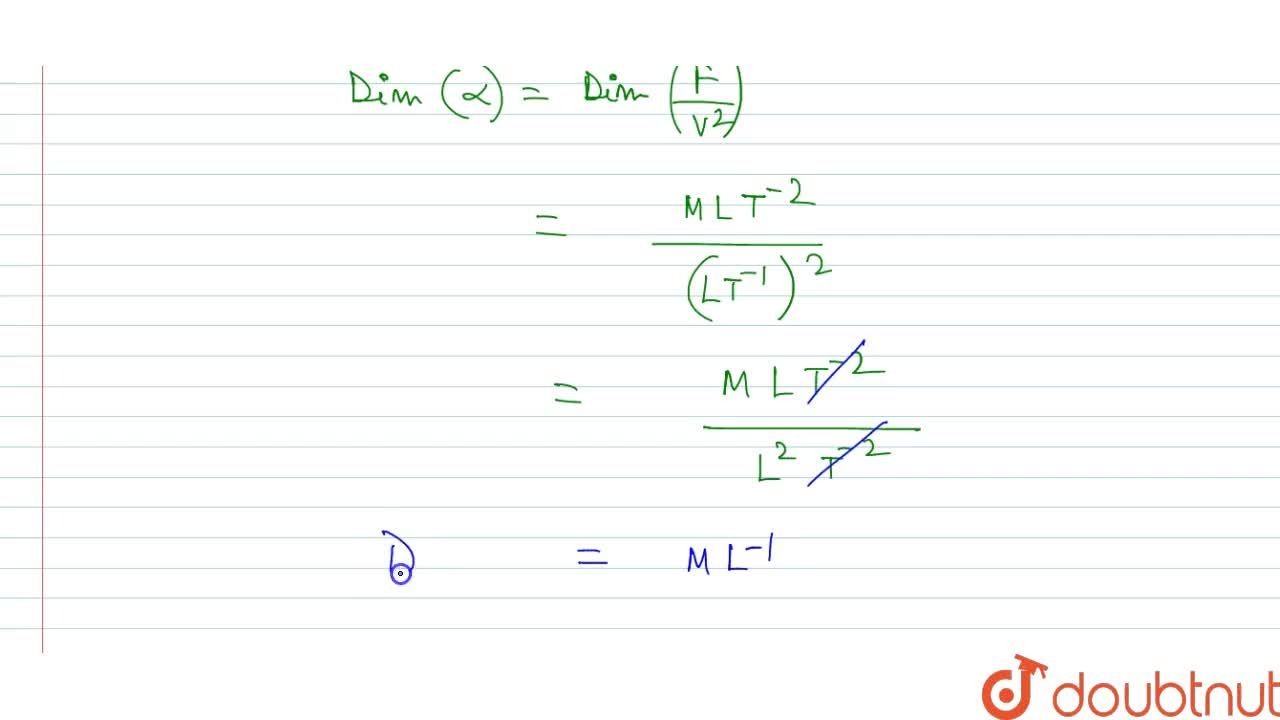
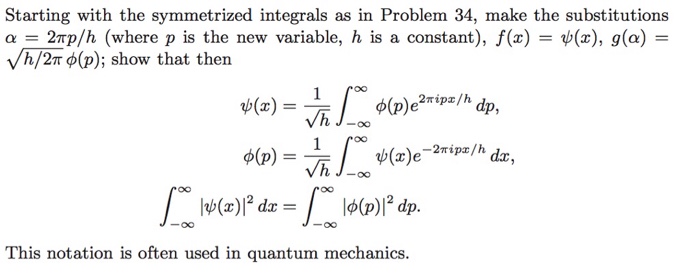



![The number of values of alpha in [0,2pi ] for which 2sin^3alpha - 7sin^2alpha + 7sinalpha = 2 is The number of values of alpha in [0,2pi ] for which 2sin^3alpha - 7sin^2alpha + 7sinalpha = 2 is](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1202186_1195942_ans_3f41dfb97833461eb1fdb950c8cffd74.jpg)